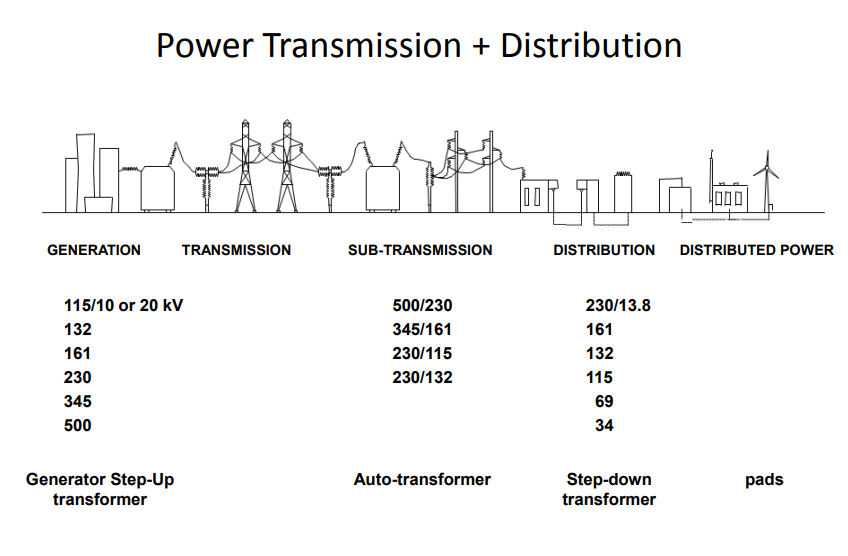
In the world of electrical engineering, transformers play a pivotal role in the transmission and distribution of electrical energy. These devices are essential for adjusting voltage levels to facilitate safe and efficient power delivery. However, to ensure their reliability and safety, it is crucial to adhere to various standard codes established by recognised organisations. This blog explores the significance of Indian Standards (IS), International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC), National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA), and American National Standards Institute (ANSI) codes applicable to electrical transformers.
What are Electrical Transformers?
Electrical transformers are static electrical devices that transfer electrical energy between two or more circuits through electromagnetic induction. They are widely used to step up (increase) or step down (decrease) voltage levels in power systems. Transformers serve critical functions in power generation, transmission, and distribution networks, making them integral to modern electrical infrastructure.
The basic operation of a transformer relies on the principle of electromagnetic induction. When alternating current (AC) flows through the primary winding, it creates a magnetic field that induces a voltage in the secondary winding. The voltage transformation ratio depends on the number of turns in the primary and secondary windings, allowing for efficient energy transfer between circuits. To Know more visit 3-Phase Transformer – Construction & Working Principle
Importance of Standard Codes
Standard codes are established to ensure safety, performance, and compatibility among electrical devices. Adhering to these standards helps manufacturers, engineers, and operators achieve the following:
Safety: Electrical transformers can pose significant hazards if not designed and operated correctly. Standards provide guidelines to minimize risks associated with electrical failures, overheating, and other potential dangers.
Performance: Standards help ensure that transformers operate efficiently and reliably, maximizing their performance in various applications. This is crucial for maintaining power quality and minimizing losses in electrical systems.
Quality Assurance: Standard codes enforce quality control measures in the manufacturing process. Compliance with these standards guarantees that transformers meet specific design, material, and testing requirements, ultimately ensuring product reliability.
Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have specific regulations governing electrical equipment. Compliance with established standards is often a legal requirement, making it essential for manufacturers and operators.
Key Standard Codes for Electrical Transformers
Indian Standards (IS)
The Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) formulates Indian Standards (IS) to promote quality and safety in various industries, including electrical engineering. Several IS codes are relevant to electrical transformers, including:
IS 2026: This standard outlines the general requirements for power transformers, covering aspects such as design, construction, testing, and performance specifications. It provides a comprehensive framework for manufacturers to follow, ensuring that transformers meet safety and performance criteria.
IS 1180: This standard specifies the requirements for distribution transformers, detailing guidelines for design, testing, and performance. Compliance with IS 1180 ensures that distribution transformers operate efficiently and safely in various applications.
International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC)
The IEC is an international standards organization that develops and publishes global standards for electrical and electronic technologies. Key IEC standards for transformers include:
IEC 60076: This series of standards provides comprehensive guidelines on power transformers, addressing design, testing, and safety considerations. The IEC 60076 standards cover various aspects, including insulation, temperature rise, and noise levels, ensuring that transformers meet international performance benchmarks.
IEC 61558: This standard focuses on the safety of transformers used in low-voltage applications. It provides guidelines for the design and construction of transformers to ensure safe operation under various conditions, including overload and short-circuit scenarios.
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA)
NEMA is an organization that establishes standards to enhance the efficiency and safety of electrical equipment. Relevant NEMA standards for transformers include:
NEMA TR 1: This standard outlines the performance specifications for transformers used in industrial applications. It includes guidelines for efficiency ratings, sound levels, and temperature rise, helping manufacturers produce high-quality transformers suitable for various industrial environments.
NEMA TR 2: This standard covers the testing requirements for transformers to ensure they meet performance expectations. Compliance with NEMA TR 2 guarantees that transformers are tested for efficiency and reliability before being deployed in the field.
American National Standards Institute (ANSI)
ANSI plays a critical role in establishing standards for electrical products in the United States. Important ANSI standards for transformers include:
ANSI C57.12.00: This standard provides general requirements for liquid-filled transformers, detailing guidelines for design, construction, and testing. Compliance with ANSI C57.12.00 ensures that transformers are built to meet safety and performance standards.
ANSI C57.12.01: This standard addresses the requirements for transformer enclosures, ensuring that they provide adequate protection against environmental factors and physical damage. It specifies the materials and design considerations necessary for durable and safe transformer enclosures.
Benefits of Compliance with Standard Codes
Enhanced Reliability: Transformers that comply with established standards are more likely to operate reliably, reducing the risk of unexpected failures and outages.
Improved Safety: Compliance with safety standards minimizes the risk of accidents and hazards associated with electrical equipment, protecting both personnel and infrastructure.
Cost-Effectiveness: By adhering to standards, manufacturers can improve production efficiency and reduce the likelihood of costly recalls or repairs due to non-compliance.
Global Acceptance: Adhering to internationally recognized standards (such as IEC and ANSI) facilitates global trade and acceptance, making it easier for manufacturers to market their products in different regions.
Challenges in Standard Compliance
While compliance with standard codes is essential, it can pose challenges for manufacturers and operators, including:
Complexity of Standards: Understanding and implementing the various codes can be complex, requiring expertise in electrical engineering and regulatory requirements.
Cost of Compliance: Achieving compliance may involve additional costs related to testing, certification, and quality assurance measures, which can be burdensome for smaller manufacturers.
Rapid Technological Changes: As technology evolves, standards may need to be updated, leading to challenges in ensuring that products remain compliant with the latest requirements.
Conclusion
Adhering to standard codes such as IS, IEC, NEMA, and ANSI is critical for the safe and efficient operation of electrical transformers. By following these standards, manufacturers and operators can ensure compliance, enhance performance, and mitigate risks associated with electrical systems.
Understanding these standards not only aids in producing reliable transformers but also contributes to the overall safety and efficiency of electrical infrastructure worldwide. As technology continues to evolve, staying informed about these standards will be crucial for anyone involved in the design, manufacture, or operation of electrical transformers.
FAQ
1. What are the key standards applicable to electrical transformers?
The key standards applicable to electrical transformers include IS (Indian Standards), IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission), NEMA (National Electrical Manufacturers Association), and ANSI (American National Standards Institute). Each provides guidelines for design, testing, and performance to ensure safety, efficiency, and reliability.
2. Why are IS standards important for transformers in India?
IS (Indian Standards) are crucial in India as they provide region-specific guidelines for the design and testing of transformers to ensure safe operation under Indian environmental and operational conditions. Compliance with IS 2026 and IS 1180 helps manufacturers meet local regulatory and performance expectations.
3. What is IEC 60076, and why is it significant?
IEC 60076 is an international standard that outlines requirements for power transformers. It covers all aspects of transformer design, testing, and safety, ensuring global compatibility and performance standards for transformers used in a wide range of applications worldwide.
4. What is the difference between NEMA and ANSI standards for transformers?
While NEMA focuses on performance specifications, particularly for industrial applications in North America, ANSI primarily deals with safety and operational standards for transformers, including design and installation requirements. Both organizations focus on safety and reliability but cater to slightly different aspects of transformer applications.
5. How do ANSI standards benefit transformer manufacturers in the U.S.?
ANSI standards provide guidelines specific to the U.S. market, ensuring that transformers meet local regulatory requirements, safety, and environmental considerations. ANSI C57.12.00 and C57.12.01 help manufacturers design transformers that meet American utility and industrial demands while adhering to safety protocols.
6. What are the key differences between IEC and NEMA standards for transformers?
IEC standards are globally recognized and focus on a broad range of transformer applications, including power and distribution transformers. NEMA standards, on the other hand, are more focused on North American markets and tend to emphasize performance in industrial environments. The main difference lies in geographic applicability and specific performance considerations.
7. How do IS standards differ from IEC standards for transformers?
IS standards (Indian Standards) are tailored to India’s electrical infrastructure and environmental conditions, while IEC standards are globally recognized and apply to a wider range of regions and conditions. IS standards often adapt IEC guidelines to suit local operational challenges, like voltage and climate considerations.
8. What is the role of testing in compliance with transformer standards?
Testing is critical for ensuring that transformers meet the required performance, safety, and reliability benchmarks set by standards like IS 2026, IEC 60076, NEMA TR 2, and ANSI C57.12.00. These tests verify aspects such as insulation, temperature rise, short-circuit behavior, and efficiency, ensuring compliance with industry guidelines.
9. Can a transformer comply with both IEC and ANSI standards?
Yes, many transformers are designed to comply with both IEC and ANSI standards, particularly if they are intended for international use. Manufacturers often ensure that their transformers meet the performance, safety, and operational guidelines of both standards to cater to a global market.
10. Why is it important for transformers to comply with NEMA standards?
NEMA standards focus on the performance and efficiency of electrical equipment used in industrial environments. Compliance ensures that transformers can handle rigorous operating conditions while maintaining energy efficiency, reliability, and noise reduction, which is critical for industries like manufacturing and automation.
Visit www.vidyutcloud.com to save your time by simplifying your electrical product and service search/purchases.
For more information on electrical transformers and their applications, subscribe to our blog or contact us for expert guidance on industry standards and best practices. Stay informed and ensure your electrical systems are compliant and efficient!